HDD vs SSD
1. HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
An HDD is a storage device that uses magnetic disks to read and write data. It is often cheaper than an SSD but has limitations in terms of speed and durability.
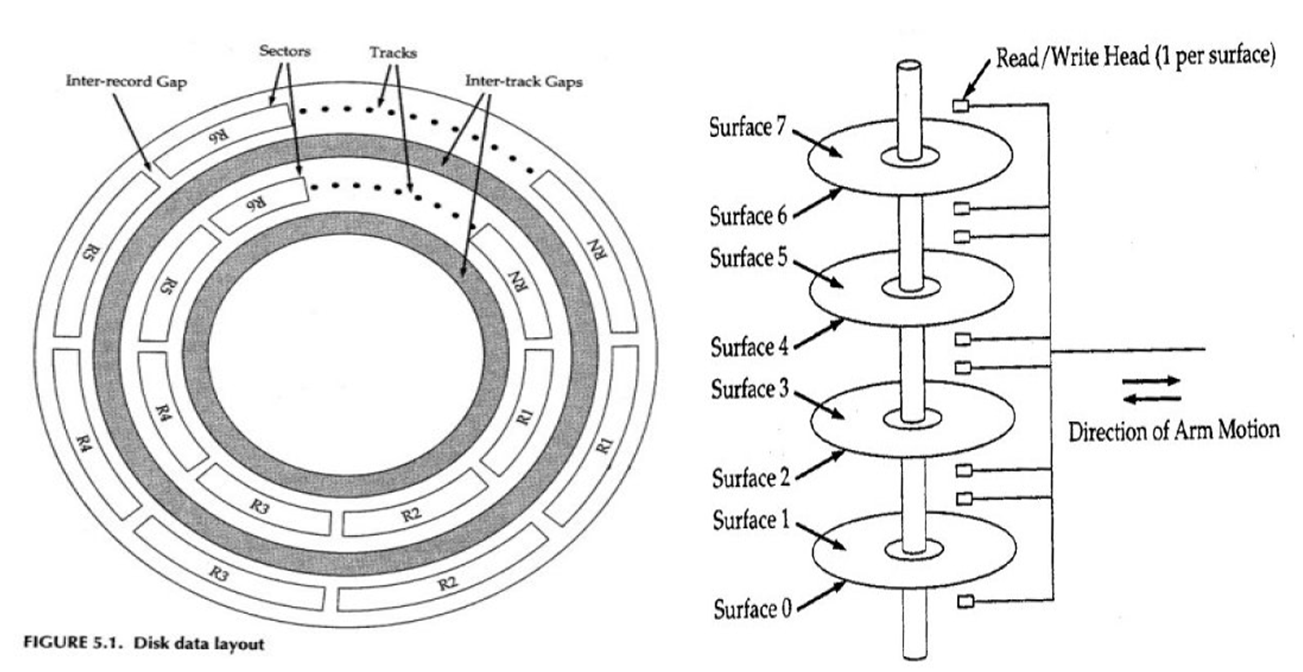
Advantages of HDD:
-
Larger Storage Capacity:
HDDs generally offer larger storage capacities, often beyond 1 TB, and can go up to 16 TB or more in some models. -
Cheaper:
The cost per GB is typically lower than that of SSDs, making HDDs a cost-effective option for users who need a large amount of storage at a lower price. -
More Write Cycles:
HDDs can handle a larger number of read and write cycles, though this is still lower than that of SSDs.
Disadvantages of HDD:
-
Slower Speeds:
HDDs typically offer slower speeds, with data transfer rates around 150 MB/s, much lower than SSDs. -
Speed Depends on RPM:
The speed is also influenced by the rotation speed of the disks:-
5400 RPM: Common speed for entry-level HDDs.
-
7200 RPM: Standard speed for most consumer HDDs.
-
10000 RPM: Faster but rarer and more expensive.
-
-
Fragility:
HDDs have moving parts (read/write heads), making them vulnerable to shocks and impacts. -
Noise:
HDDs generate noise during operation due to the rotation of disks and movement of the heads.
2. SSD (Solid State Drive)
An SSD is a storage device that uses flash memory chips to store data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, which provides several benefits.
Advantages of SSD:
-
High Speed:
SSDs are much faster than HDDs, with data transfer speeds varying depending on the type:-
SATA: Up to 500 MB/s.
-
PCIe: Up to 1500 MB/s or higher with modern models.
-
mSATA: Similar to SATA, around 500 MB/s.
-
-
Durability:
SSDs have no moving parts, making them more robust against shocks, vibrations, and physical wear. -
Silent Operation:
SSDs are completely silent, as there are no moving parts.
Disadvantages of SSD:
-
Lower Storage Capacity:
SSDs generally offer lower storage capacities compared to HDDs for a similar price. Larger SSDs (over 1 TB) can be expensive. -
More Expensive:
SSDs are typically more expensive per GB compared to HDDs, although this price difference is narrowing over time. -
Limited Write Cycles:
SSDs have a limited number of write/erase cycles, though this number has improved significantly in recent years, and they generally offer enough durability for most users (around 3000 to 5000 cycles of data block erasure).
Summary Comparison HDD vs SSD
| Criterion | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Larger (up to 16+ TB) | Smaller (up to 4+ TB) |
| Price | Cheaper | More expensive |
| Speed (Data Transfer) | 150 MB/s (on average) | 500 MB/s (SATA), up to 1500 MB/s (PCIe) |
| Noise | Noisy | Silent |
| Durability | Fragile (moving parts) | Very durable (no moving parts) |
| Lifespan | Good, but limited by disk rotation speed | Excellent (more write cycles) |
| Recommended Use | Large-scale storage on a budget | High performance, gaming, heavy applications |
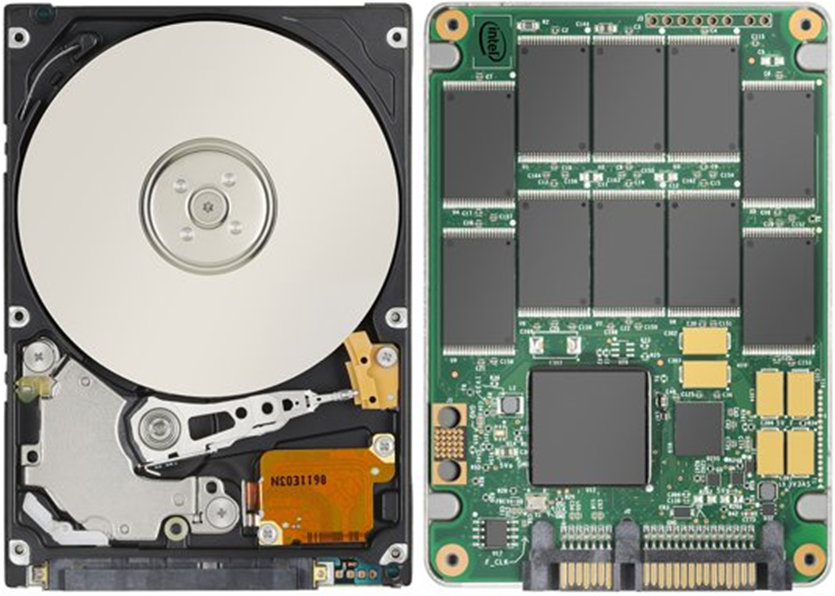
Conclusion
-
If you're looking for affordable storage with large capacity, an HDD remains a solid choice.
-
If you need fast performance, silence, and robustness, an SSD is the better option, though it comes at a higher cost per GB.