The Computer Working Environment
1. Definition
The computer working environment refers to all the hardware and software elements that the user sees, interacts with, and uses when working on a computer.
It includes:
-
Input and output devices (mouse, keyboard, screen…),
-
The graphical user interface (desktop, icons, windows…),
-
System and application software,
-
As well as the internal hardware components (CPU, memory, storage…).
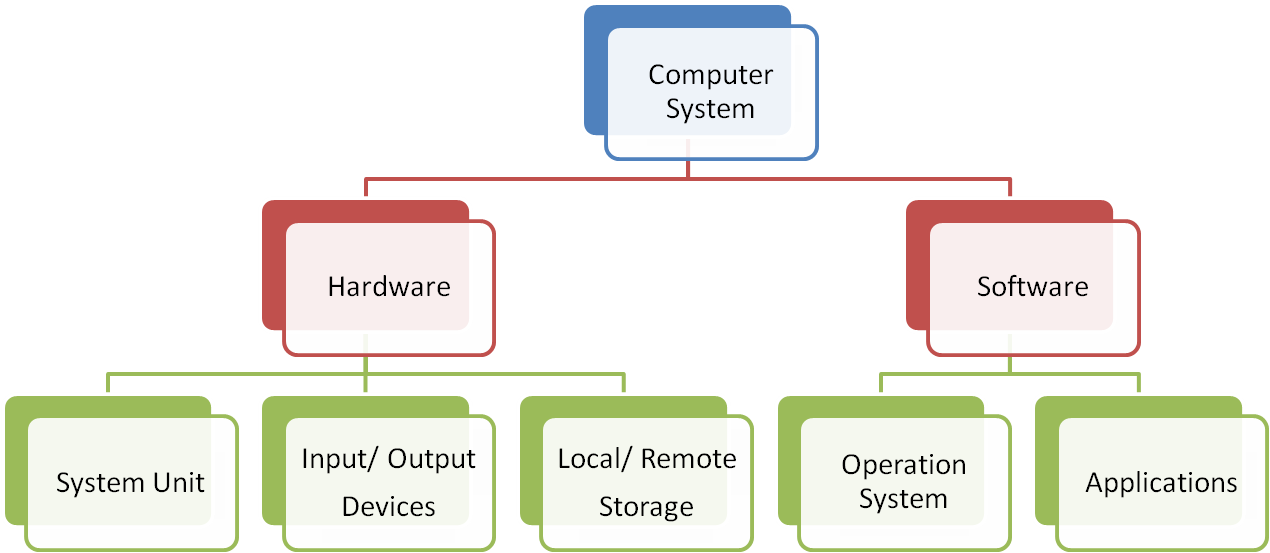
2. Hardware Components
These are the physical parts of the computer. They fall into three main categories:
a. Input devices
Used to enter data into the computer:
-
Keyboard: for typing text.

-
Mouse: for navigating and interacting with items on the screen.

-
Scanner
 , webcam
, webcam , microphone
, microphone , etc.
, etc.
b. Output devices
Used to display or output results:
-
Monitor (screen): displays visual information.

-
Printer
 , speakers
, speakers  , etc.
, etc.
c. Internal components
These ensure the internal functioning of the computer:
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU): the brain of the computer.
-
Random Access Memory (RAM): temporary memory for active processes.
-
Hard Drive or SSD: for long-term data storage.
-
Motherboard, power supply, graphics card, etc.
3. Software Components
These are the non-physical (digital) parts of the environment.
a. Operating System (OS)
Manages both hardware and software resources. It provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for easy interaction. Examples: Windows, macOS, Linux.
c. Application Software
Programs that allow the user to perform specific tasks:
-
Word processors (e.g., Word), Web browsers (e.g., Chrome), Media players, etc.
4. Importance of Understanding the Working Environment
Knowing your environment helps to:
-
Work more efficiently,
-
Avoid common errors,
-
Make the most of digital tools.