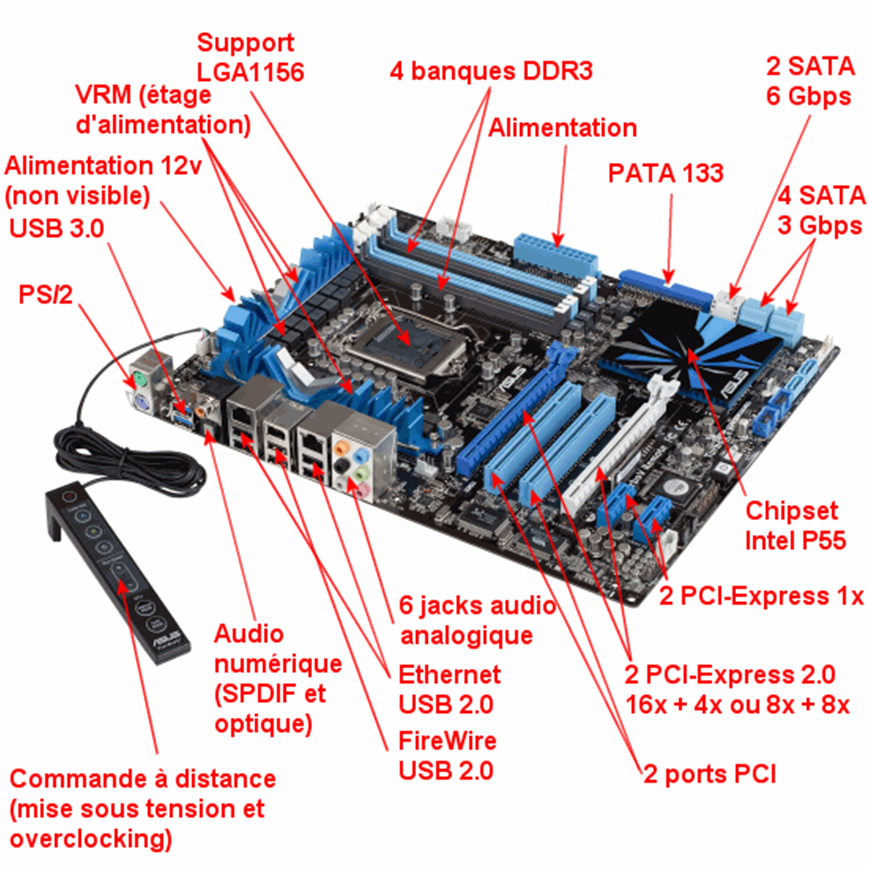
Connectors and Wireless Connections
Introduction
Connectors are essential components for establishing communication between devices in a computing environment. These can either be wired or wireless, enabling data exchange, multimedia transmission, and other forms of interaction between hardware devices.
1. Wired Connections
-
USB Port (Universal Serial Bus):
-
The USB port is one of the most common interfaces for connecting various devices to computers, such as keyboards, mice, printers, and storage devices. It supports both data transfer and power supply.
-
Versions: USB has evolved over time, with USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB-C offering different speeds and functionalities. USB-C is the most modern version, offering high-speed data transfer, video output, and power delivery through a single connector.
-
-
Ethernet Port (RJ45 Connector):
-
The Ethernet port, typically using the RJ45 connector, is used for wired network connections. It connects computers, printers, or routers to a local area network (LAN) for high-speed internet or intranet access.
-
Speed: Ethernet connections offer various speeds, such as 10/100/1000 Mbps, with modern networks supporting up to 10 Gbps.
-
-
VGA Port (Video Graphics Array):
-
The VGA port is an older video connection standard used to transmit analog video signals to displays such as monitors or projectors.
-
Resolution: VGA supports resolutions up to 1920x1080 (Full HD), but its analog nature limits its quality compared to newer digital connections like HDMI.
-
-
HDMI Port (High Definition Multimedia Interface):
-
HDMI is a digital connection standard used to transmit both video and audio signals to monitors, televisions, projectors, and other multimedia devices.
-
Features: HDMI supports high-definition video, including 4K, and multi-channel audio. It is widely used in home entertainment systems, gaming consoles, and computers.
-
2. Wireless Connections
-
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity):
-
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or local networks without the need for physical cables. It uses radio waves to transmit data between routers and devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
-
Speed and Range: Modern Wi-Fi technologies, such as Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), offer faster speeds and better range compared to older versions.
-
-
Bluetooth (Short-Range Radio Technology):
-
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect and exchange data over short distances (typically up to 100 meters).
-
Applications: Bluetooth is commonly used for connecting peripheral devices like wireless keyboards, mice, headphones, and speakers to computers or mobile devices.
-
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of wired and wireless connections is crucial for modern computing. Wired connections such as USB, Ethernet, VGA, and HDMI provide reliable, high-speed, and high-quality data transfer, while wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer the flexibility of connecting devices without physical cables. The choice of connector depends on the specific needs of the devices and the environment.