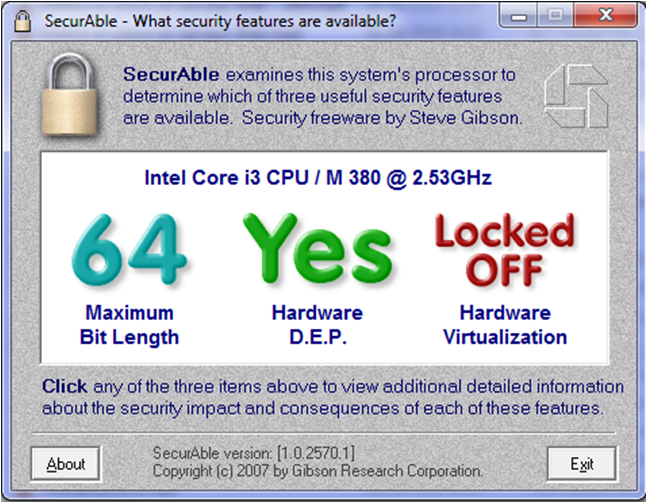
32 bits vs 64 bits
1. What is the bit count?
-
The number of bits refers to the width of the processor's data bus, indicating how many bits of data the processor can process at a time.
-
A 32-bit system processes 32 bits of data simultaneously, while a 64-bit system processes 64 bits at once.
2. Memory Limitations
-
32-bit system:
-
The maximum memory addressable by a 32-bit system is 2^32 bytes, or 4 GB of RAM.
-
In practice, the system uses part of this memory for management, so the actual accessible memory is usually around 3.25 GB.
-
-
64-bit system:
-
A 64-bit system can theoretically address 2^64 bytes, which is an astronomical amount of memory, far greater than what current computers can provide. Practically, 64-bit systems allow for the use of more than 4 GB of RAM.
-
3. Running 32-bit Programs on a 64-bit System
-
A 32-bit program can run on a 64-bit system, but it will be limited by the memory constraints of a 32-bit program (typically 2 GB to 3 GB maximum).
-
A 64-bit program cannot run on a 32-bit system.
4. Advantages of a 64-bit System
-
Access to more RAM: A 64-bit system allows for the use of more RAM, essential for tasks like video editing, 3D modeling, large databases, etc.
-
Better performance: 64-bit processors can handle larger data and perform computations more quickly.
-
Compatibility with modern software: More and more software is being developed for 64-bit systems, offering better performance and more features.
📌 Summary
| Feature | 32-bit System | 64-bit System |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Memory | 4 GB (2^32) | Practically unlimited (2^64) |
| Actual Accessible Memory | ~ 3.25 GB | More than 4 GB |
| Program Execution | 32-bit programs can run | 64-bit programs required for higher memory |
| Performance | Limited by 32-bit memory and processors | Improved performance with 64-bit processors and systems |